The Early Mississippian Village at the Bruce Catt Site
Arkansas State University Research Station Arkansas Archeological Survey The Early Mississippian settlement pattern in northeast Arkansas consists of dispersed villages of varying size. Site distribution is strongly correlated with well-drained sandy soils of the Dundee-Bosket-Dubbs and the Amagon-Dundee soil associations. Besides being well-drained, these are some of the best soils for growing crops like maize. Around A.D. 800 there appear to be multiple ethnic groups experimenting with new ceramic techniques such as shell tempering and red slipping, and creating new vessel forms including funnels, seed jars, and beakers. These groups practiced horticulture that included some maize production. They hunted with the bow and arrow, another newly introduced technology in the mid-South, and fished with bone harpoons.
Varney Red is an Early Mississippian pottery type first identified by Stephen Williams in 1954 based on archaeological research in southeast Missouri. Dan and Phyllis Morse describe Varney Red as having “a heavy clay and hematite slip applied to the interior surfaces of large shallow pans, small to large globular jars, and bowls. Hooded bottles (or seed jars) were slipped on the exterior.” The slip was probably applied to “waterproof” the vessel (Morse and Morse 1990:56).
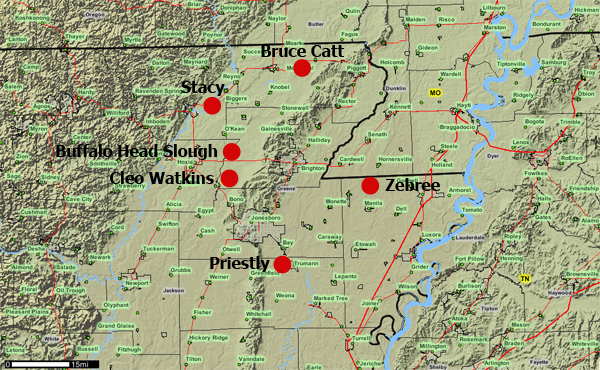
Sites with excavated Early Mississippian components in Southeast Missouri and Northeast Arkansas include Hoecake in the Cairo Lowland, which Morse and Morse (1990) think is the earliest emergence of Mississippian culture; the Kersey, Varney, and Zebree sites in the Eastern Lowlands; Gooseneck and Owls Bend in the eastern Missouri Ozarks; and Bruce Catt, Stacy, Priestly, Cleo Watkins and Buffalo Head Slough in the Western Lowlands. Excavations at Zebree, a 1-hectare (2.47 acres) Big Lake Phase village, were conducted in the late 1960s through 1970s. Morse, along with several Arkansas Archeological Society members, salvaged another 1-hectare (2.47 acres) village at the Cleo Watkins site in 1987, which also contains some Early Mississippian deposits. Several years earlier, in 1984, Morse salvaged the Stacy site on Black River in Clay County. This site consisted of at least three separate Early Mississippian farmsteads; pit features yielded an abundance of Varney Red ceramic sherds. The Priestly site, a .5-hectare (1.2 acre) village with fewer houses than Zebree, was excavated in the late 1980s under the supervision of David Benn of the Center for Archaeological Research at Southwest Missouri State University. In 1997, with the help of Survey and Society members, I excavated pit and post features at Buffalo Head Slough which also contained an Early Mississippian component as evidenced by Varney Red rimsherds from flared rim jars.
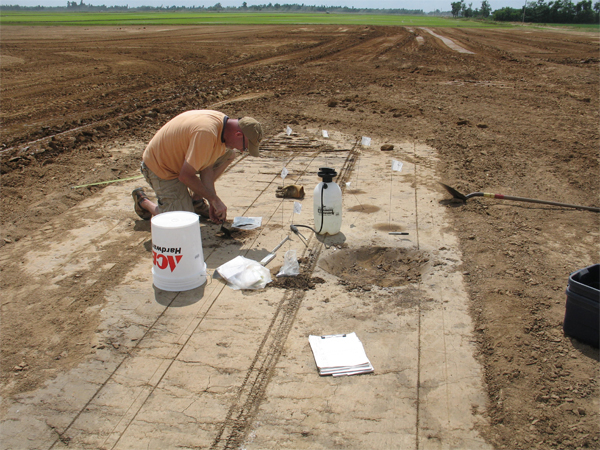
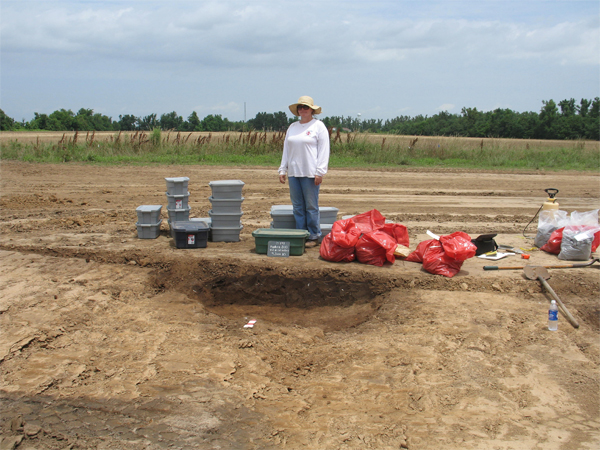
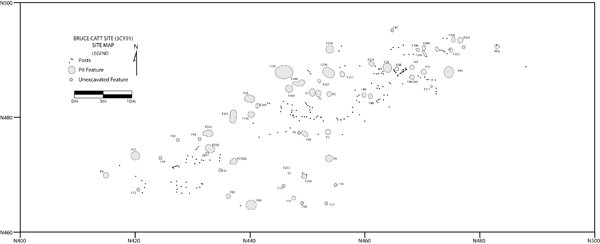
In May of this year, I entered into an agreement with landowner Randy Bolen and the tenant, Bruce Catt, to excavate features at the Bruce Catt site (3CY91) as the site was being land leveled. We made preparations for the land leveling and on Friday afternoon, May 7, 2010, three dirt buggies began leveling the field. Approximately 6 to 9 feet of soil would eventually be removed from the apex of the site. The site was leveled very gradually over a period of a month. Different areas were exposed at different times based on when the dirt buggies were available to remove the plowzone. The majority of the 310 features we documented are Mississippian period trash pits and house posts.
The fill from most features was removed from the site and water-screened through 1/4 inch or 1/8 inch hardware cloth. Flotation samples were removed from nearly every excavated feature. There was little super-positioning of features. In only three cases did we observe a post within a pit and in no case were pits superimposed, though Features 1 and 2 were immediately adjacent to one another. A small, shallow prehistoric trash pit near the center of the site with a square historic post contained a nail and a brick fragment from an early historic occupation of the site.
The spatial arrangement of posts was not easy to decipher. Houses were not nice squares like we have seen at so many other Early Mississippian sites.
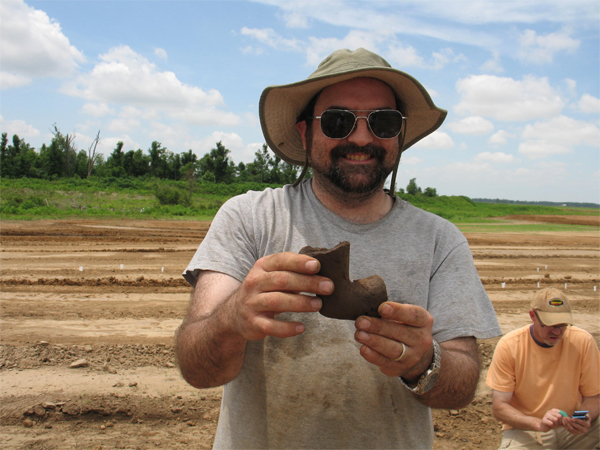
Because of my fetish with Mississippian trash, we rarely encounter museum quality artifacts. This pipe is an exception. It was found by Dorian Kettler, the first president of the Central Mississippi Valley chapter of the Society, who is shown here.
Another atypical discovery that day was made by Scott and Tony when they shoveled into a large pit feature just west of Dorian’s pipe, and came up with a mass of charred plant material. Preliminary analysis of this material by archaeobotanist Dr. Elizabeth Horton suggests that this may be bundles of plant material for basket construction. We wrapped this and numerous other samples of charred plants in foil.
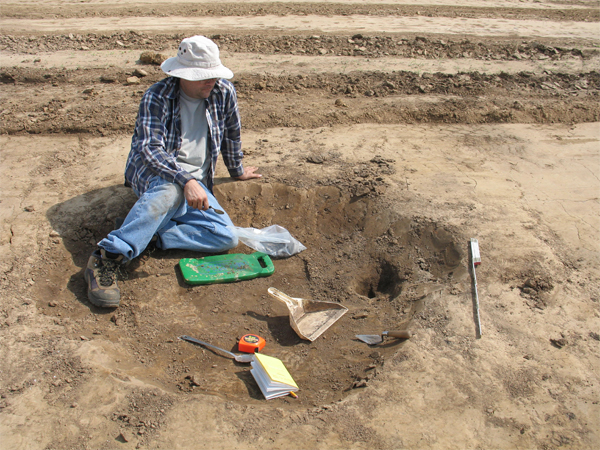
This is Shelley Bonner excavating one of the larger pit features we excavated at the site.
Here is Shelley standing in the largest feature at the site, Feature 310.
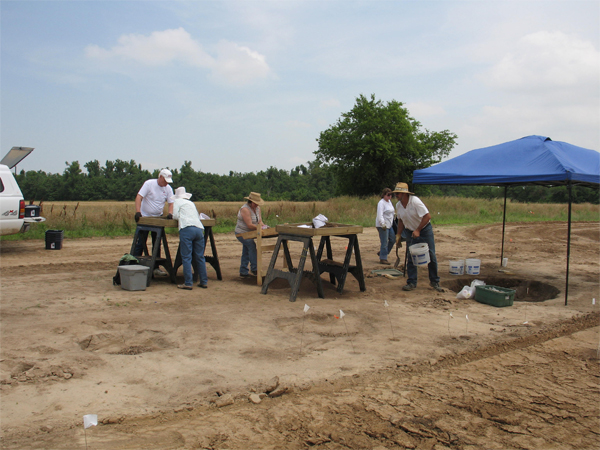
Volunteers, Arkansas State University students, and Society members helped excavate Pit Feature 43. From left to right are David and Patsy Terrell, Diana Angelo, Shelley Bonner and John Riggs. The dirt buggies were continuously rolling as we worked. On hot and windy days the dust from the dry field would sometimes blow in the direction we were working, so where we worked on a given day would depend on the prevailing wind.
As part of the faunal identification workshop at the 2010 Society Training Program, we identified the following species collected from Feature 43: canids (wolf, coyote, dog), raccoon, skunk, mink, possum, rabbit, deer, squirrel, rodents, multiple species of fish and turtle, birds (turkey, owl, ducks), and snake (Colubridae).
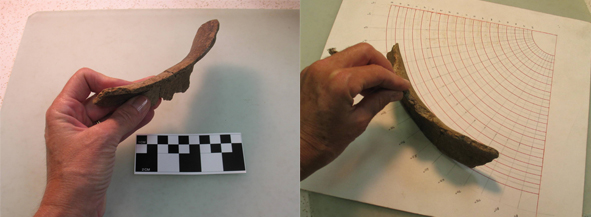
This is a large Varney Red jar rim fragment, refitted from three sherds.
Several features yielded cord marked, shell tempered sherds, as well as some sand tempered sherds attesting to the Early Mississippian temporal assignment.
Two shell tempered clay elbow pipes were recovered.
Numerous shell gastropod beads were found in several different trash pits, including Features 219 and 43. A small sample of recovered freshwater mussels identified by Bob Scott include species that would be expected in the Cache River Basin. The common names for several of these species are rather interesting: Black sandshell, Wabash pigtoe, Pyramid pigtoe, Three ridge, Bleuffer, Muckett, Spike, Plain pocketbook, Fatmucket, and Pistolgrip.
Very few diagnostic Early Mississippian chipped stone artifacts have been observed in materials so far processed, but they include one arrow point tip fragment and numerous older whole and fragmentary spear points. Lithic raw materials are dominated by Crowley’s Ridge chert which is locally available, just a few kilometers east of the site.
Bone tools are numerous and so far I have observed at least 4 deer ulna awls and other modified bone tools and objects. I expect we will find more stone and bone tools as more material is washed, sorted, and examined. The southernmost portion of the Bruce Catt site is totally destroyed, but thanks to the landowner and farmer, the Survey was able to salvage a tremendous amount of information about what life was like in the Early Mississippian period in this part of the Cache River Valley. All of the materials recovered from the site have been washed and sorted and are currently being inventoried by ASU Station Assistant Bob Scott and Arkansas State University students. Analyses of the spatial arrangement of pits and posts, including the materials they contained: pottery, stone tools and debris, faunal remains and plant remains will make it possible to compare and contrast this significant Early Mississippian site with others in the region. One thing that has yet to be done is to obtain radiocarbon dates from some of the features at the site. Obtaining absolute dates for the site will enhance the pre-contact era chronological framework for Northeast Arkansas and Southeast Missouri. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|